News • Trial results surpass expectations
AI enhances breast cancer screening performance
New research results now published from Lund University’s MASAI trial are even better than the initial findings from last year:

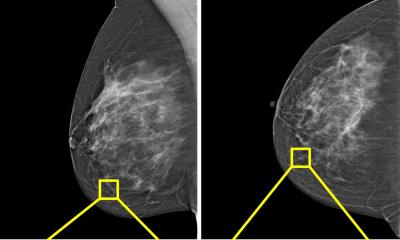
Image source: Lund University; photo: Ingemar Hultquist
AI-supported breast screening detected 29% more cases of cancer compared with traditional screening. More invasive cancers were also clearly detected at an early stage using AI. Now the final part of the research study will focus on breast cancer missed by screening. The new findings are published in The Lancet Digital Health.
The initial results of the Mammography Screening with Artificial Intelligence (MASAI) study – a randomised trial to evaluate whether AI can improve mammography screening – were published in August 2023. The study started in spring 2021, and the final report will be written next year. A second report has now been published, and Kristina Lång, who is responsible for the study, is pleased to be able to show strong figures.
“Since the first report last year, the number of cancers detected by AI-supported screening has gone from being 20% more to 29% more than those found by traditional screening,” says Kristina Lång, researcher and associate professor of diagnostic radiology at Lund University, Sweden and consultant at the Unilabs Mammography Unit in Malmö.
Every year, around one million women are called for mammography screening in Sweden. The mammogram are reviewed by two breast radiologists – a medical skill that is currently in short supply. In the MASAI trial, AI had to identify mammograms with an increased risk of breast cancer. These cases were then reviewed by two breast radiologists. Other mammograms were only reviewed by one breast radiologist. In all these cases, the radiologist(s) was/were assisted by AI, which highlighted suspicious findings on the image.
Recommended article
News • Safety analysis
AI-supported mammography found to be safe and workload-saving
A new safety analysis finds AI-supported mammography analysis is as good as two breast radiologists working together to detect breast cancer, almost halving the screen-reading workload.
The new research report is based on results from almost 106,000 women screened for breast cancer. Half of them were randomly assigned to undergo traditional mammography screening, while the other half received AI-supported screening. AI-supported screening was found to pick up not only more cancers overall (in 338 people compared with 262) but also 24% more early-stage invasive cancers (in 270 people compared with 217).
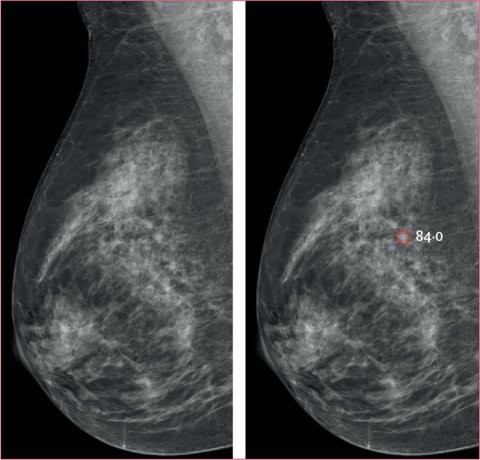
Image source: Hernström V, Josefsson V, Sartor H et al., Lancet Digital Health 2025 (CC BY 4.0)
“They also included relatively more aggressive cancers that are particularly important to detect early. At a later stage, the prognosis may have deteriorated and more intensive treatment is often required,” says Kristina Lång, pointing to potential benefits in terms of reduced suffering, higher survival rates and lower economic costs if these cancers can be detected more frequently at an early stage.
Pre-cancerous lesions, known as in situ cancers, were also more likely to be detected with AI – 51% more such cases were found (68 people compared with 45). A large proportion of the additional in situ cases found were of the more severe type which also benefits from early detection.
Importantly in this context, the number of false positives did not rise despite an increase in cancer detection. “A false positive is when a woman is recalled for work up but is then found not to have cancer. This can be a stressful experience for women participating in screening. But only seven more people, corresponding to a 1% increase, received these false alarms in the AI-supported group compared with the control group,” says Kristina Lång.
As in the previous report from last year, AI-supported screening was again found to significantly reduce breast radiologists’ workload by 44%.
Sweden has a generous screening programme by international standards. All women aged 40-74 years are invited for a mammogram every 1.5-2 years. However, the interval between two screening visits can be long enough for cancer to be diagnosed – even if the last screening was considered normal. These so called interval cancers is the next group of cancers that Kristina Lång and her colleagues will analyse. “This December, the 106,000 women have been followed up for two years, allowing researchers to see how common it is to receive a breast cancer diagnosis between two screening visits. Our hope is that AI will prove helpful here too,” says Kristina Lång.
Results from the MASAI trial have already contributed to the implementation of AI support in several regional screening programs in Sweden.
Source: Lund University; by Erika Svantesson
06.02.2025