World first for liver transplant team
A transplant team at a Birmingham hospital has achieved a world first after resuscitating a liver that would have previously been considered unviable.
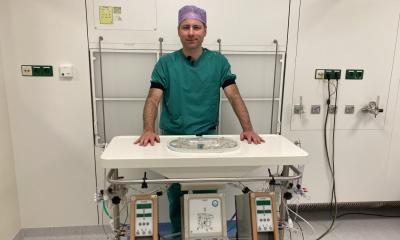
Surgeons at Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham successfully revived the organ for transplantation by pumping oxygenated blood through it after a journey of more than 200 miles inside an ice box.
The liver, which was recovered from a cardiac death patient, had taken seven hours to arrive in Birmingham, a delay which would have significantly increased the risk of graft failure if the transplant was carried out in the conventional way.
However, after being resuscitated using the “warm blood” machine, the surgical team at QEHB, which carries out nearly 200 liver transplants a year, was able to transplant the revived liver into a patient who had been on the waiting list for a new organ.
Although other transplant centres around the world have carried out the same resuscitation technique on discarded livers, or tested similar procedures on animal models, the team at QEHB became the first in the world to successfully transplant a revived liver graft from a cardiac death donor into a patient.
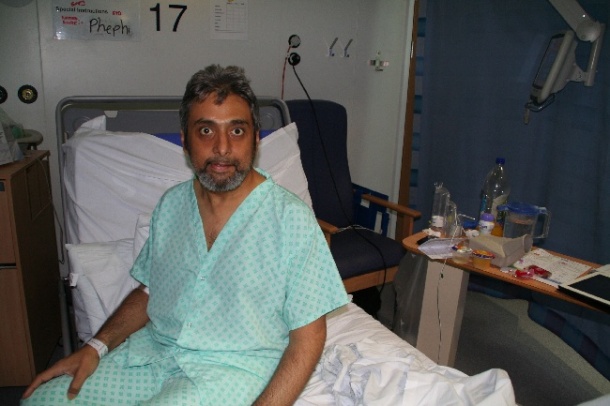
Mr Satpal Mahal, aged 46, from Walsall in the West Midlands, who had liver cirrhosis, was discharged from QEHB just 11 days after receiving his new liver.
The entire process took around 18 hours from the organ first being retrieved to completion of the transplant operation. It involved a team of around a dozen UHB staff led by consultant liver transplant surgeons Mr Thamara Perera, Mr Paolo Muiesan and Mr Hynek Mergental, consultant anaesthetist Dr Hentie Cilliers, and theatre staff.
Mr Perera, who performed the operation, said: “There has been recent interest within the liver transplant community about the use of various machine devices to ‘pump blood’ at body temperature into organs retrieved from donors because it has been shown to minimise the damage which is inevitable when organs are preserved in cold storage.
“Many options and different combinations of techniques are proposed and currently under investigation in various clinical studies and trials.
“Several centres in the world are currently investigating the possibility of this type of warm resuscitation at the end of cold storage. However this was the first successful transplant.
“There are other centres that have been testing this technique on animals and discarded livers that are deemed unsuitable for transplantation.
“Our centre initially carried out tests on discarded livers before we got to this stage. The liver unit at QEHB is now performing three different approaches to revive organs from deceased donors which is a unique achievement.”
Mr Perera said they carried out the resuscitation procedure on the liver using a machine called Organ Assist, funded by the hospital’s own QEHB Charity.
Mr Mergental, who assisted in the procedure, has set up this facility of testing livers over the last few months.
“In the instance of a cardiac death donor there will be initial damage to the person’s organs because the oxygen supply has stopped, in this case for nearly two hours, although reasonable blood supply was maintained during this period,” he added.
“In the current standards this liver graft would have been rejected and discarded.
“We can preserve these organs in cold storage but only up to about eight hours in the case of a cardiac death donor as the chance of organ failure is much higher beyond this period. There is also an increased chance of liver failure after the transplant.
“In this particular case the organ was transported to QEHB in an ice box so it was seven hours before it arrived at the hospital for transplanting.
“This was considered too long for the transplant operation to be carried out in the conventional way – from the cold storage directly in to the recipient – so it was decided to resuscitate this organ on the machine using ‘warm blood’.
“If we had used the liver in the normal way then the chance of failure would have been high.”
Mr Perera said the machine, which also contains an oxygenator, works by constantly pumping blood at body temperature into the liver through two blood vessels in the organ.
“The warm blood revitalises the liver by taking out the coldness from being in an ice box, but also nourishes it through the oxygenated blood. It is able to simulate the blood supply within a real body.
“One advantage of this technique is that surgeons can actually choose the only grafts that would work on the machine, thereby preventing a graft failure once a transplant is carried out.
“Within the first 90 minutes of using the machine all the parameters became normal, so a collective decision was taken by the surgical and anaesthetic team to transplant this liver.
“When the transplant operation was completed the liver was resuscitated for a further seven hours on the machine, but his immediate outcome was comparable to any other patient receiving a straightforward transplant.”
Mr Perera said the hospital trust had previously given approval for the new procedure in April this year but this was the first time they were able to test it.
The transplant recipient, former company boss Mr Mahal, said he was enjoying life as a “world breaker”.
Mr Mahal, who was managing director of his own import and export business prior to his illness, said: “I was very confident even though this was a new procedure.
“I knew that I was in the best place with the right physicians and staff. And I have been told that it has been very successful, so it’s a world breaker.”
Mr Mahal said problems with his liver were first diagnosed almost three years ago, but his condition deteriorated to the point where he was put on the transplant waiting list for a new organ about two months ago.
28.08.2014