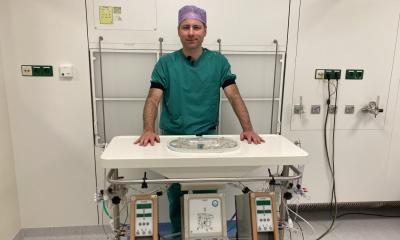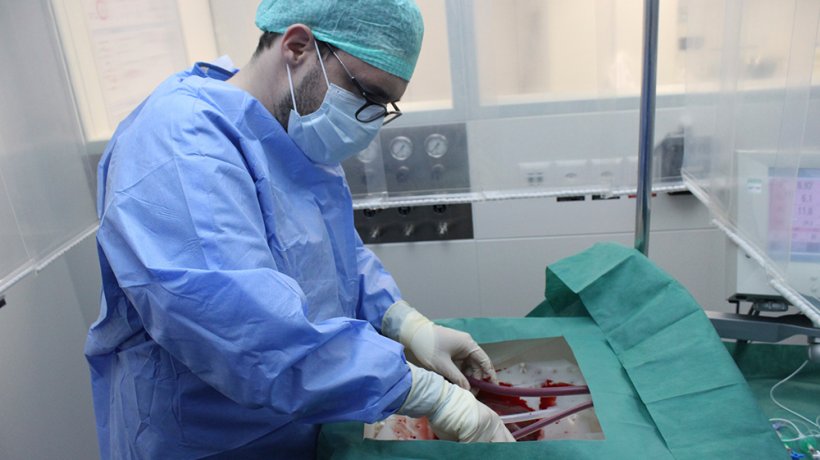
Image source: USZ/beamue
News • Transplant breakthrough
Machine keeps liver alive for one week outside of the body
Researchers from the University Hospital Zurich, ETH Zurich, Wyss Zurich and the University of Zurich have developed a machine that repairs injured human livers and keeps them alive outside the body for one week. This breakthrough may increase the number of available organs for transplantation, saving many lives of patients with severe liver diseases or cancer.
Until now, livers could be stored safely outside the body for only a few hours. With the novel perfusion technology, livers - and even injured livers - can now be kept alive outside of the body for an entire week. This is a major breakthrough in transplantation medicine, which may increase the number of available organs for transplantation and save many lives of patients suffering from severe liver disease or a variety of cancers. Injured cadaveric livers, initially not suitable for use in transplantation, may regain full function while perfused in the new machine for several days. The basis for this technology is a complex perfusion system, mimicking most core body functions close to physiology. The corresponding study was now published in the journal Nature Biotechnology.
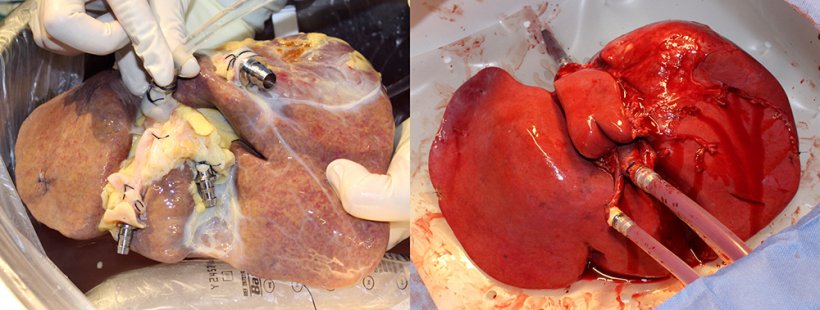
Image source: USZ/beamue
"The success of this unique perfusion system - developed over a four-year period by a group of surgeons, biologists and engineers - paves the way for many new applications in transplantation and cancer medicine helping patients with no liver grafts available," explains Prof. Pierre-Alain Clavien, Chairman of the Department of Surgery and Transplantation at the UniversityHospital Zurich (USZ). When the project started in 2015, livers could only be kept on the machine for 12 hours. The seven-day successful perfusion of poor-quality livers now allows for a wide range of strategies, e.g. repair of preexisting injury, cleaning of fat deposits in the liver or even regeneration of partial livers.
The Liver4Life project was developed under the umbrella of Wyss Zurich institute, which brought together the highly specialized technical know-how and biomedical knowledge of experts from the UniversityHospital Zurich (USZ), ETH Zurich and the University of Zurich (UZH). "The biggest challenge in the initial phase of our project was to find a common language that would allow communication between the clinicians and engineers," explains Prof. Philipp Rudolf von Rohr, professor of process engineering at ETH Zurich and co-leader with professor Clavien of the study.
The inaugural study shows that six of ten perfused poor-quality human livers, declined for transplantation by all centers in Europe, recovered to full function within one week of perfusion on the machine. The next step will be to use these organs for transplantation. The proposed technology opens a large avenue for many applications offering a new life for many patients with end-stage liver disease or cancer.
Source: University of Zürich
14.01.2020