Increasing incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus
A new study from researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center and the Dallas Veterans Affairs Medical Center shows the relation between chronic acid reflux and malignant mutation - and why an accurate therapy of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is of major importance.
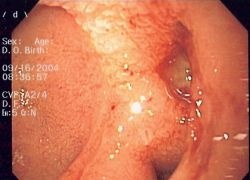
“The more reflux you have and the longer you have it, the more it might predispose you to getting Barrett’s esophagus,” said Dr. Ronda Souza, associate professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern.
The chronic reflux of gastric components damages the esophagus. Cells divide more frequently to regenerate the structure but each time the telomeres at the end of DNA shorten. “When they become too short, the esophagus can’t regenerate the normal skin-like squamous cells anymore,” the scientists suppose, after comparing telomere length and telomerase activity in biopsy specimens taken from 54 patients. Instead intestinal-like cells are recruited to the area.
“Those cells are acid-resistant but unfortunately more prone to cancer. They could be cells circulating from the bone marrow, which can turn into intestinal tissue,” explained Dr. Spechler, professor of internal medicine. Dr. Spechler and colleagues demonstrated that bone-marrow cells play a decisive role to regenerate esophageal lining in rats that suffer heavy reflux.
“None of this is absolutely proven, but it’s an interesting concept, and it certainly supports the theory that your normal cells poop out and you get Barrett’s esophagus, which tends to turn malignant,” said Spechler. That underscores the importance of preventing recurring acid reflux.
13.08.2007