Four-stranded helix identified in human cells
Quadruplexes may turn instrumental in devising new targeted therapies
Sixty years ago, a research paper was published which was the first to describe the double-helix DNA structure.
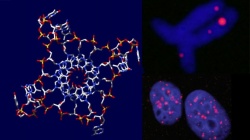
That discovery had been made by James Watson and Francis Crick from the University of Cambridge in the UK. After ten years of investigations, researchers from the same university have now gone public with a paper proving the existence of quadruple structures in the human genome (http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/four-stranded-quadruple-helix-dna-structure-proven-to-exist-in-human-cells/). The work, published in Nature Chemistry, shows links between concentrations of four-stranded quadruplexes and DNA replication, which plays a key role in cell division and production.
Scientists believe that targeting quadruplexes with synthetic molecules which trap and contain these DNA structures can prevent cells from replicating their DNA, blocking cell division and halting cell proliferation at the root of cancer. The research „indicates that quadruplexes are more likely to occur in genes of cells that are rapidly dividing, such as cancer cells“, said Prof. Shankar Balasubramanian whose group produced the research. According to the expert from the University of Cambridge’s Department of Chemistry and Cambridge Research Institute, four-stranded structures and their potential for targeted cancer treatment are to serve as a new paradigm for investigation. (Michael Reiter)
30.01.2013