Radiotherapy
Prostate: Free of cancer after five years
Results from a randomised controlled trial to compare the use of permanent radioactive implants (brachytherapy) with dose-escalated external beam radiotherapy in patients with prostate cancer show that the men who received brachytherapy were twice as likely to be cancer-free five years later. These results presented Professor James Morris, from the Department of Radiation Oncology, Vancouver Cancer Centre, at the 3rd ESTRO Forum in Barcelona, Spain.
Morris pointed out that the ASCENDE-RT1 trial is the first and only existing trial comparing low-dose-rate prostate brachytherapy (LDR-PB) for the curative treatment of prostate cancer with any other method of radiation therapy delivery.
The trial enrolled 398 men with cancer that had not spread outside the prostate gland who were judged to be at high risk of treatment failure, based on standard tests for a number of features of the cancer. The patients initially received androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), aimed at reducing levels of the male hormones that stimulate prostate cancer cells to grow. After eight months of ADT, all patients received 46 Gy2 of external beam radiotherapy to the prostate and regional lymph nodes.
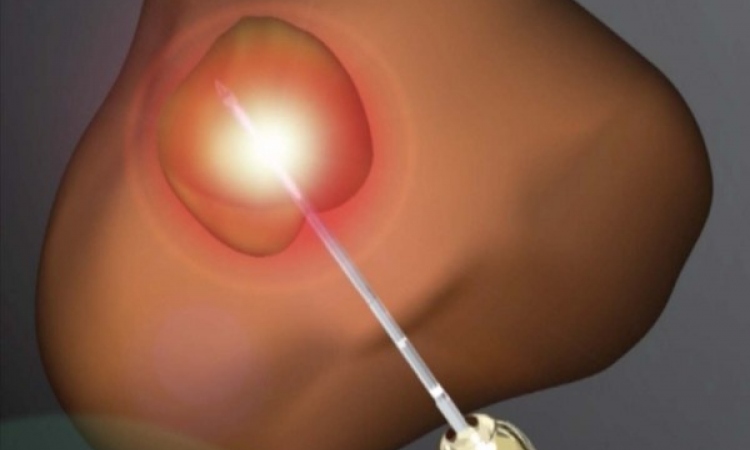
Following this, 198 men received LDR-PB in which tiny radioactive seeds were implanted in the prostate gland while under general or spinal anaesthesia. The other 200 patients were randomised to dose-escalated external beam radiation therapy (DE-EBRT) and received an additional 32 Gy of external beam radiation to achieve a total prostate dose of 78 Gy.
“At five years follow up, we saw a large advantage in progression-free survival in the LDR-PB group,” Prof Morris will say. “Although, to date, overall survival and prostate cancer-specific survival do not appear to differ between the two groups, existing trends favour LDR-PB and an overall survival advantage is likely to emerge with longer follow-up.”
LDR-PB is an extremely cost-effective treatment, the researchers say, but it does require prolonged training and experience in order to produce consistent results, and this may limit more widespread adoption. An additional problem is that, in the trial, the LDR-PB patients experienced more urinary side effects that those who received DE-EBRT.
At BCCA’s five cancer centres, LDR-PB boost is now regarded as the standard of care for unfavourable risk localised prostate cancer. “The ideal next step,” Prof Morris will say, “would be to undertake randomised comparisons of LDR-PB boost against its principal alternatives – temporary high-dose-rate brachytherapy implants (HDR-PB)3, stereotactic body radiation therapy using extreme hypofractionation4, and combined surgery and post-operative radiation therapy. “In the meantime, ASCENDE-RT has made an important contribution to the search for a more effective curative treatment for prostate cancer,” he concluded.
1. Androgen Suppression Combined with Elective Nodal and Dose Escanodal and Dose Escalated Radiation Therapy.
2. A Gray, or Gy, is a measure of radiation dose, defined as the absorption of one joule of energy per kilogram of tissue.
Morris: abstract no. OC-0485: “LDR Brachytherapy is Superior to 78 Gy of EBRT for Unfavourable Risk Prostate Cancer: The Results of a Randomized Trial.”
Source: ESTRO
04.05.2015