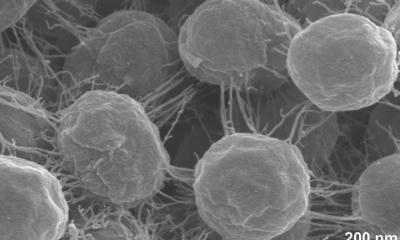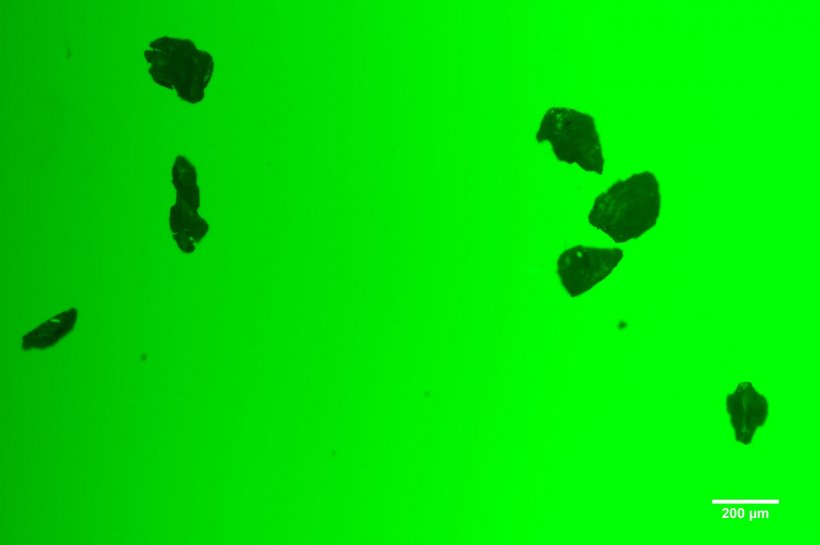
Image courtesy of the Alvarez Research Lab
News • Hazardous materials
Microplastic pollution aids antibiotic resistance
According to scientists at Rice University’s George R. Brown School of Engineering, discarded polystyrene broken down into microplastics provides a cozy home not only for microbes and chemical contaminants but also for the free-floating genetic materials that deliver to bacteria the gift of resistance.
A study in the Journal of Hazardous Materials describes how the ultraviolet aging of microplastics in the environment make them apt platforms for antibiotic-resistant genes (ARGs). These genes are armored by bacterial chromosomes, phages and plasmids, all biological vectors that can spread antibiotic resistance to people, lowering their ability to fight infections.
Recommended article
News • Altering the intestinal microbiome
How nanoplastics threaten human health
A recent review study concludes that nanoplastics change the composition and diversity of gut microbiome in vertebrates and invertebrates. The effects of a widespread and prolonged exposure to nanoplastics observed in animal models can be applied to humans.
The study led by Rice civil and environmental engineer Pedro Alvarez in collaboration with researchers in China and at the University of Houston also showed chemicals leaching from the plastic as it ages increase the susceptibility of vectors to horizontal gene transfer, through which resistance spreads. “We were surprised to discover that microplastic aging enhances horizontal ARG,” said Alvarez, the George R. Brown Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering and director of the Rice-based Nanotechnology Enabled Water Treatment Center. “Enhanced dissemination of antibiotic resistance is an overlooked potential impact of microplastics pollution.”
The researchers found that microplastics (100 nanometers to five micrometers in diameter) aged by the ultraviolet part of sunlight have high surface areas that trap microbes. As the plastics degrade, they also leach depolymerization chemicals that breach the microbes’ membranes, giving ARGs an opportunity to invade. They noted that microplastic surfaces may serve as aggregation sites for susceptible bacteria, accelerating gene transfer by bringing the bacteria into contact with each other and with released chemicals. That synergy could enrich environmental conditions favorable to antibiotic resistance even in the absence of antibiotics, according to the study.
Source: Rice University
03.12.2021