Article • Plethora of questions
DIAM guides vital IT decisions
Which is the best way to implement imaging IT in a hospital? How can new technologies be integrated into existing IT infrastructures? What risks are associated with our systems?
Report: Sascha Keutel
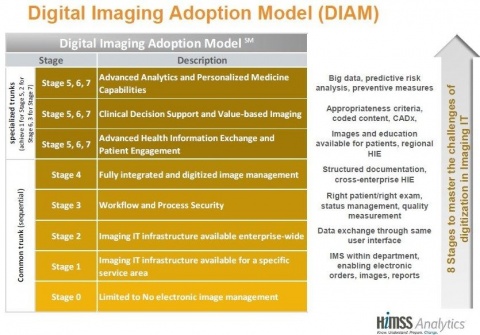
The Digital Imaging Adoption Model (DIAM) is a new benchmark ‘designed to support healthcare facilities with the analysis, planning and implementation of a digital strategy in their imaging departments,’ explains Dr Peter Mildenberger, Professor of Radiology at Mainz University Hospital, in Germany, who is also the initiator of the annual DICOM meeting held in Mainz.
Partners HIMSS Analytics in Europe and the European Society of Radiology (ESR) presented the model to the healthcare community at ECR 2016. ‘While using a similar approach as EMRAM, DIAM goes far beyond the EMRAM parameters,’ Mildenberger points out.
A scoring system defines parameters in 10 areas
DIAM encompasses eight stages of a digital imaging adoption strategy with 0 denoting ‘low maturity’ and seven ‘advanced maturity’. A scoring system of more than 100 indicators defines parameters in ten areas, such as software infrastructure, health information exchange, workflow and process security, quality and safety management or patient engagement.
‘In a way,’ Mildenberger explains, ‘it’s a self-assessment of the participants. They complete a survey covering general data, such as department size, number of employees and exams, etc. However, it also includes questions regarding a RIS, or the link between department and RIS, the use of language recognition, and it asks how many reports are processed and when.’
However, benchmarking specific equipment or employees is not within the scope of the analysis. The participating facility receives the results of the analysis – a detailed report on the strengths and weaknesses of the IT structure surveyed, including potential areas of investment or specific compliance objectives for each stage. What’s in it for a hospital? With the project still in the pilot phase in Mainz University Hospital, and several European facilities, a definite assessment is not yet available.

Assessing any problems in the infrastructure
Professor Mildenberger is, however, sure that DIAM can support users and buyers of imaging technologies with their operative and strategic decisions. ‘It’s important for decision makers to see whether their institution has a well-crafted infrastructure, or whether there are problems lurking that nobody has noticed yet, or where the improvement potential is. ‘Last, but not the least, DIAM can help hospital management to pursue the right digital strategy when planning or investing in IT projects.’ Experts from HIMSS Europe or ESR are available to support these endeavours.
Profile:
Professor Peter Mildenberger, Senior Resident at the radiology clinic in Mainz University Hospital, heads Image Data Management in which he is responsible for all operations. His particular interests lie in radiological software applications – image processing, archiving and communication systems (PACS), telemedicine, eHealth, and eLearning.
09.08.2016