Journey to the stomach
The journey into the self becomes reality: Siemens Healthcare and Olympus Medical
Systems Corporation announce collaborative development of advanced magnetically
guided capsule endoscope system for intragastric observation Siemens Healthcare and Olympus Medical Systems Corporation are collaborating on the development of a technology for a magnetically guided capsule endoscope (MGCE) system.
This innovative technology is intended to allow stomach examinations to be performed easily and comfortably by having the patient simply swallow an endoscope in the form of a capsule. The patient would then lie down in a magnetic guidance system. It is envisioned that the physician, via a joystick, will then be able to navigate the capsule easily to the areas of interest and that the capsule will provide real-time high-resolution images on a display in the examination room.
"In cooperation with our partner Olympus, we usher a new era in endoscopy. We believe that the magnetically guided capsule endoscope will enable quick examinations that are comfortable for the patient. This system will be an excellent addition to current methods in endoscopy, for instance within the scope of aftercare," said Hermann Requardt, CEO of Siemens Healthcare.
“As a leading manufacturer of endoscopes, Olympus is continuously working to develop products that can be used safely and with confidence. Our aim is to create endoscopes that minimize the stress on patients and that are user-friendly for physicians. Capsule endoscopes have excellent potential from these perspectives. We see this joint development project with Siemens as the realization of one of our visions for the future of capsule endoscopes,” said Haruhito Morishima, President, Olympus Medical Systems Corporation.
Traditionally capsule endoscopes are moved only by peristaltic motion in the gastrointestinal tract.
This often makes it difficult to guide the capsule to a specific location, and examinations are
therefore limited to confined areas of the gastrointestinal tract, such as the small intestine. Thereare many medical cases that involve the gastrointestinal tract beyond the small intestine, and capsules designed for use in the small intestine can not be used for thorough examinations of the large internal cavity.
Siemens Healthcare and Olympus Medical Systems Corp. are therefore developing a technology that is intended to allow the physician to steer a capsule interactively to observe any location in the stomach. Siemens Healthcare, one of the world's largest suppliers to the healthcare industry and a trendsetter in medical imaging, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems, together with Olympus, the world’s leading manufacturer of endoscopes and innovative solutions for many healthcare disciplines, are combining their most advanced technologies for the new project. Both companies are jointly developing the capsule endoscopy unit, the magnet guidance system, and the image processing and guidance information systems. Currently the two providers have developed a prototype which will be used to determine the safety, effectiveness and benefits of this new generation of endoscopic technology.
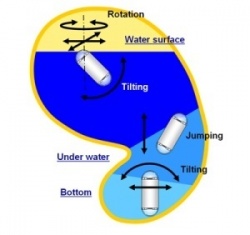
Features of the prototype capsule endoscope, image processing and guidance information system and guidance magnet: The capsule endoscope will be approximately 31mm long and 11mm in diameter. Camera systems mounted at both ends of the capsule are intended to allow observation inside the stomach. Realtime observation will be made possible by means of captured images, which will be transmitted to an image processing system, and guidance information on the posture of the capsule endoscope as it is navigated by magnetic guidance. During the examination, the patient’s stomach will be filled with water to provide a field of vision for the capsule endoscope and enable navigation. The patient will be positioned within the guidance magnet, placing the stomach of the patient with the capsule endoscope in the center of the system.
It is anticipated that the physician will control the motion of the capsule with a joystick. It will be possible to tilt and rotate the capsule and move it horizontally and vertically.
It is conceptualized that guidance magnet will generate magnet fields that vary over time, making it possible to steer the capsule as desired in real-time. The intensity of those magnetic fields is between those of magnetic resonance scanners and the basic field of the earth.
04.05.2010