Sensor
Technology for examining cardiovascular blood vessels
For the examination of coronary blood vessels, intravascular methods with imaging technologies are already state-of-the-art. However, ultrasonic methods, which are used to gather information about the tissue, can only be used externally, up to now. The piezo electronical components necessary for this have not been sufficiently miniaturized to be inserted into the blood vessels.
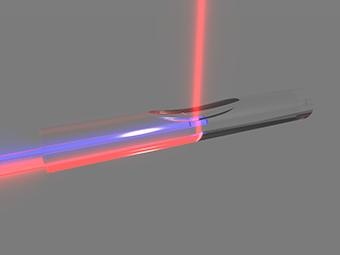
The Laser Zentrum Hannover e.V. (LZH) and the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology would like to change this. This group of researchers are thus working on an opto-acoustical sensor for medical ultrasonic technology.
For reliable cardiological diagnostics, intravascular examinations are indispensable. This minimal invasive surgical interventions insert optical sensors directly into the coronary blood vessels and enable a more detailed image of the vessel than could be made using external investigation methods.
Opto-acoustical sensor for detailed images
Now, the scientists want to combine intravascular diagnostics with ultrasonic technology. However, the piezo electronical components necessary for this have not yet been sufficiently miniaturized. For this reason, the new technology is based on optical interferometry:
The intravascular module should be equipped with an opto-acoustical imaging sensor which can provide an internal image of the tissue of the coronary blood vessels up to a depth of 1 mm. To achieve this, a guided laser impulse from an illuminating fiber is first absorbed by the blood vessel tissue. The resulting ultrasonics are then guided to a fiber-based ultrasonic detector via an acoustical lens.
By transforming this signal into an optical signal, a complete image of the vascular walls can be made. An optical interferometer recognizes deviations in the reflection pattern, making the detection of abnormal or disease-based changes in the tissue possible.
The diagnosis of diseases and disorders, for example arteriosclerosis, will be much simpler since this sensor should have a significantly higher sensitivity and resolution, in comparison to present methods. Also, the use in other areas is being considered. Optical interferometry should be examined as an alternative to present ultrasonic detections, including the use for technical applications.
Process Engineering from the LZH
The scientists in the Laser Micromachining Group are developing the process engineering necessary for the production of the acoustical lenses. These will be inserted directly into the glass substrate. In order to do so, specific areas of the substrate will be removed first using the laser, and then polished.
Further parts of the intravascular sensor module are, apart from the lens, an ultrasonic detector element, and a lighting fiber for ultrasonic stimulus. The design and the conversion of the signals into an image which can be used for diagnostics is being developed by the scientists at the Technion.
The research project „Integrated silica-based photoacoustic probe for intravascular imaging via laser micro-machining and interferometric sensors“ is being jointly led by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Ludger Overmeyer (LZH) and Ass. Prof. Amir Rosenthal (Technion). It will be supported by the state of Lower Saxony until the beginning 2019 within the course of the funding initiative “Niedersächsisches Vorab”.
Source: Laser Zentrum Hannover e.V. (LZH)
03.05.2016