Immunology
New antibody therapy improves psoriasis symptoms
Only a single treatment produced what researchers describe as 'rapid, substantial, and durable clinical improvement'.
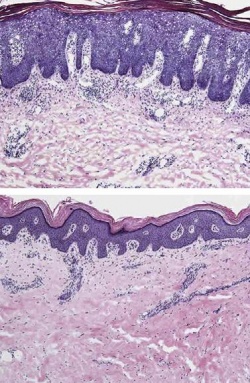
Many patients suffering from psoriasis showed significant recovery after just a single dose of an experimental treatment with a human antibody that blocks an immune signaling protein crucial to the disease, researchers report. By the end of the trial, conducted at Rockefeller University and seven other centers, nearly all of the 31 patients to receive treatment saw dramatic, if not complete, improvement in their symptoms.
"The striking result we achieved using a human antibody that targets the signal interleukin-23 suggests we are on the threshold of doing something very different from our current model of treating psoriasis with immunosuppressive drugs throughout an adult lifetime," says study author James Krueger, director of the Milstein Medical Research Program, D. Martin Carter Professor in Clinical Investigation and head of the Laboratory of Investigative Dermatology. "It raises the possibility of working toward long-term remission -- in other words, a cure." The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology published the results on Thursday (March 12).
Psoriasis is a debilitating disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly turns on the skin, producing red, itchy, scaly patches. In 2004, Krueger and colleagues suggested a dominant role for interleukin-23 in the disease, and research since then has supported this hypothesis. It appears that interleukin-23, a type of immune signaling molecule known as a cytokine, kicks off a cascade of interactions that leads to inflammation in the skin and excessive growth of skin cells and dilation of blood vessels.
The discovery of interleukin-23's role has led to tests of a number of new antibody-based therapies that target it, but the compound, known as BI 655066, stands out. BI 655066 is a human antibody that targets interleukin-23 and blocks it from binding to the receptors on cells that respond to it. Only a single treatment produced what the team describes as "rapid, substantial, and durable clinical improvement in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis." On average, patients who received the treatment had a more than 80 percent improvement in the severity and extent of their skin lesions that continued until tracking ended six weeks after treatment. Meanwhile, genetic sequencing from skin samples revealed that the antibody's action reduced the expression of many of the cytokines and other molecules that define psoriasis.
Source: Press release Rockefeller University
16.03.2015